Oracle uses two engines to process PL/SQL code. All procedural code is handled by the PL/SQL engine while all SQL is handled by the SQL statement executor, or SQL engine.
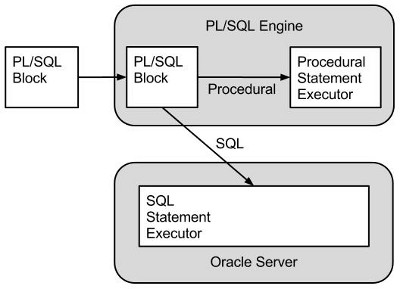
There is an overhead associated with each context switch between the two engines. If PL/SQL code loops through a collection performing the same DML operation for each item in the collection it is possible to reduce context switches by bulk binding the whole collection to the DML statement in one operation.
1- create test1 table and it's constraint and set timing on to watch the period of execution
Bulk binds can also improve the performance when loading collections from a queries. The

There is an overhead associated with each context switch between the two engines. If PL/SQL code loops through a collection performing the same DML operation for each item in the collection it is possible to reduce context switches by bulk binding the whole collection to the DML statement in one operation.
1- create test1 table and it's constraint and set timing on to watch the period of execution
CREATE TABLE test1( id NUMBER(10), description VARCHAR2(50)); ALTER TABLE test1 ADD ( CONSTRAINT test1_pk PRIMARY KEY (id)); SET TIMING ON
----------
DECLARE
TYPE id_type IS TABLE OF test1.id%TYPE;
TYPE description_type IS TABLE OF test1.description%TYPE;
t_id id_type := id_type();
t_description description_type := description_type();
BEGIN
FOR i IN 1 .. 10000 LOOP
t_id.extend;
t_description.extend;
t_id(t_id.last) := i;
t_description(t_description.last) := 'Description: ' || To_Char(i);
END LOOP;
FOR i IN t_id.first .. t_id.last LOOP
INSERT INTO test1 (id, description)
VALUES (t_id(i), t_description(i));
END LOOP;
FOR i IN t_id.first .. t_id.last LOOP
UPDATE test1
SET description = t_description(i)
WHERE id = t_id(i);
END LOOP;
FOR i IN t_id.first .. t_id.last LOOP
DELETE test1
WHERE id = t_id(i);
END LOOP;
COMMIT;
END;
/
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
Elapsed: 00:00:60.00
-----
Using the FORALL construct to bulk bind the inserts this time is reduced around 18 seconds.
DECLARE
TYPE id_type IS TABLE OF test1.id%TYPE;
TYPE description_type IS TABLE OF test1.description%TYPE;
t_id id_type := id_type();
t_description description_type := description_type();
BEGIN
FOR i IN 1 .. 10000 LOOP
t_id.extend;
t_description.extend;
t_id(t_id.last) := i;
t_description(t_description.last) := 'Description: ' || To_Char(i);
END LOOP;
FORALL i IN t_id.first .. t_id.last
INSERT INTO test1 (id, description)
VALUES (t_id(i), t_description(i));
FORALL i IN t_id.first .. t_id.last
UPDATE test1
SET description = t_description(i)
WHERE id = t_id(i);
FORALL i IN t_id.first .. t_id.last
DELETE test1
WHERE id = t_id(i);
COMMIT;
END;
/
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
Elapsed: 00:00:42.05
A collection must be defined for every column bound to the DML which can make the code rather long winded, but the performance improvements more than make up for this.
Bulk binds can also improve the performance when loading collections from a queries. The
BULK COLLECT INTO construct
binds the output of the query to the collection. To show this we must first load our table with some data.DECLARE
TYPE id_type IS TABLE OF test1.id%TYPE;
TYPE description_type IS TABLE OF test1.description%TYPE;
t_id id_type := id_type();
t_description description_type := description_type();
BEGIN
FOR i IN 1 .. 10000 LOOP
t_id.extend;
t_description.extend;
t_id(t_id.last) := i;
t_description(t_description.last) := 'Description: ' || To_Char(i);
END LOOP;
FORALL i IN t_id.first .. t_id.last
INSERT INTO test1 (id, description)
VALUES (t_id(i), t_description(i));
COMMIT;
END;
/
----
Populating two collections with 10,000 rows using a FOR..LOOP takes approximately 1.02 seconds.
DECLARE
TYPE id_type IS TABLE OF test1.id%TYPE;
TYPE description_type IS TABLE OF test1.description%TYPE;
t_id id_type := id_type();
t_description description_type := description_type();
CURSOR c_data IS
SELECT *
FROM test1;
BEGIN
FOR cur_rec IN c_data LOOP
t_id.extend;
t_description.extend;
t_id(t_id.last) := cur_rec.id;
t_description(t_description.last) := cur_rec.description;
END LOOP;
END;
/
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
Elapsed: 00:00:01.02
Using the BULK COLLECT INTO construct reduces this time to approximately 0.01 seconds.
DECLARE
TYPE id_type IS TABLE OF test1.id%TYPE;
TYPE description_type IS TABLE OF test1.description%TYPE;
t_id id_type;
t_description description_type;
BEGIN
SELECT id, description
BULK COLLECT INTO t_id, t_description FROM test1;
END;
/
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
Elapsed: 00:00:00.01
Yasser

No comments:
Post a Comment